Docker Installation and Usage Example
Cybersecurity if you work in the field, you need to have a very wide range of deep knowledge as well as constantly continue your development. Last year, if you followed software development trends Docker you may have heard of ‘a lot. DevOps you may notice that developers working in the field talk about containers, isolated machines, hypervisors, and they often talk about them. Here in this article is one of the above statements, “Why we need containers“, we’ll talk about that.
What is Docker?
What Docker actually does is separate application code from infrastructure requirements. You can do this, every app “containers It does this by operating in an isolated environment called ”. Docker is a software solution developed to create comprehensive applications.
On Docker’s own site, Docker is described as follows:
“A container image is a lightweight, stand-alone, executable package of a piece of software that includes everything needed to run it: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries, settings.“
Why Docker?
To explain this with an example; There may be problems around us when software developed by institutions goes live for everyone to use. If the developed code does not work on the system, you may have heard the comments of the software developer as “but it was running on my computer. The reasons for such problems generally arise from forgetting some requirements/side programs required for the operation of the project. This was one of the main reasons for the Docker solution.
Each Docker container begins its life like a naive baby who knows nothing. Next, we tell the containers everything they need to know and they find out. Everything we want him to learn and do Dockerfile we specify in the file.
Before diving into the world of Docker, let’s take a look at Docker’s structural tools.

Docker has four main tools to do what is asked of it:
- Docker Engine (https://docs.docker.com/engine/)
- Docker compose (https://docs.docker.com/compose/overview/)
- Docker machine* (https://docs.docker.com/machine/overview/)
- Docker Swarm (https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/)
Docker Engine
Docker Enginea Dockerfile or docker-compose.ymlcreates and runs images by taking information from ‘. Docker CLI over a “dockerwhen it uses the ” command, it contacts the Docker Engine to perform the necessary operations.
Docker compose
Docker compose; It is used to run structures consisting of multiple microservices, databases and similar dependencies. docker-compose.yml, it allows us to configure all the necessary services in one place and create and run them all with a single command.
Docker machine
More than one Docker Engine engine can be managed in Docker. Docker machine‘allows you to install Docker Engine on remote machines and manage the remote Docker Engine from your own computer.
Docker Swarm
Docker Swarmcontainer for Docker platform orchestration it is intermediary. With Docker Swarm, you can manage your applications with large coverage consisting of components such as databases, application servers and web servers, and scaling can be easily done under load.
What is a Virtual Machine?
Virtual machine (VM) is the virtualized version of a real machine. It simulates the hardware of a machine inside a larger machine. So, you can run many virtual machines on a larger server. Inception if you’ve watched the movie, it might be a better reenactment. You may remember that in the movie, dreams were seen within dreams. The process done here is to run (different) machines(s) within the machine. What makes VMs work Hypervisor it is a great software known as.
What is Hypervisor?
Virtual machines can only work because they have the Hypervisor program. It is special software that allows a physical machine to host virtual machines with several different or the same features. All VMs can run their own programs within themselves and use the hardware the host has. However, there is an important thing to know here, Hypervisor determines the resources required for VMs to use.
Note: VirtualBox a VMware if you cannot create a virtual machine even though you have installed a virtualization software like this, there may be two reasons. The first reason may be due to the lack of virtualization feature of your processor. The second reason is, BIOS over Hyper-V it may be due to the feature not being activated.
“Virtual machines have been in our lives for a long time and we use them a lot, why are they so preferred even though containers suddenly appear?We encounter questions like ” a lot. Completely removing virtual machines from our lives can have good and bad consequences. Of course, we cannot argue that virtual machines are bad or unnecessary, but it is obvious that their management is quite difficult and costly.
If you are someone who works in the DevOps field or know people who work in this field, you may have the idea that their job is extremely difficult. Virtual machines need a lot of storage and RAM resources. Apart from these, the much more important issue is the issue of time. Since the installation stages of virtual machines are no different from installing an operating system on a normal machine, they require a lot of time to install, create and be ready for use.
Hackers and DevOps engineers are actually very lazy (no errors in similes). If something needs to be repeated many times, we want to automate it and sit back and enjoy ourselves. That’s why automating something is so important to us.
Development, testing, etc. with Docker You can quickly create installations of environments and spend all the time you used to lose to install these environments focusing on your improvements. Docker hub you can find the images you need and them 3-5 minutes at most you can start using it inside.
Previously, you also had to install utility programs or libraries on the virtual machine that your application needed to run. If you forgot one of these programs or libraries when you moved the application elsewhere, you could think about the problem for hours. With Docker, all programs and libraries can now be packaged as an image, reproduced and used as many times as desired without any problems.
Docker shares the resources given to it (CPU, RAM, etc.). When Docker shares a CPU, everyone thinks they’re using the entire resource. This is one of the most common misconceptions about Docker. When Docker is granted CPU usage permission, it does not use the entire CPU resource and does not load the system. File systems may vary depending on the specific operating systems prepared within Docker images. Prepared containers may have different names and different network interfaces. Containers prepared with Docker recognize themselves as the only working system on the computer and are not aware of other working containers.
Docker Setup How To?
Installing Docker is extremely easy. Almost all systems (*Unix, Windows, MacOSIt has support for ‘. We are in this narrative Linux Ubuntu 16.04 we will install it on the operating system distribution.
Let’s update our repo before installing.
$ sudo apt-get updateNext, let’s use the following command to install Docker:
$ sudo apt-get install -y docker.ioWith the above commands, we easily installed Docker on the Ubuntu operating system.
You can run the following command to ensure that the Docker installation is completed and the service is running:
$ sudo systemctl status dockerIf the output of the command is as follows, our Docker service is now working without any problems.
● docker.service – Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2019-04-14 14:55:05 +03; 4h 42min ago
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 1778 (dockerd)
Tasks: 14
Memory: 116.0M
CPU: 9.358s
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─1778 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// –containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Docker service not working (i.e. “InactiveIf ”) and you want the service to run at startup, you can use the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start docker && sudo systemctl enable dockerDocker command “sudoyou need to run it with ”. However, if you add your existing user to the Docker group, you can run it without using the “sudo” command. For this, when you are in the terminal with your own user:
$ sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
$su – ${USER}The above command will add your current user to the Docker group. “ to test the accuracy of the action taken and in general to find out the groups your user is involved inid -ngYou can use the ” command.
MacOS installation https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-mac/install/ to his file from here
Windows installation you can access the file here https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/
Image and Container
Docker image and containers you may find that their terms are sometimes used interchangeably, but as a term they both express different explanations.
Docker imagesthey are executable packages that contain everything necessary to run an application. It contains codes, library files, variables and configuration files.
Docker containerit occurs after the operation of an image.
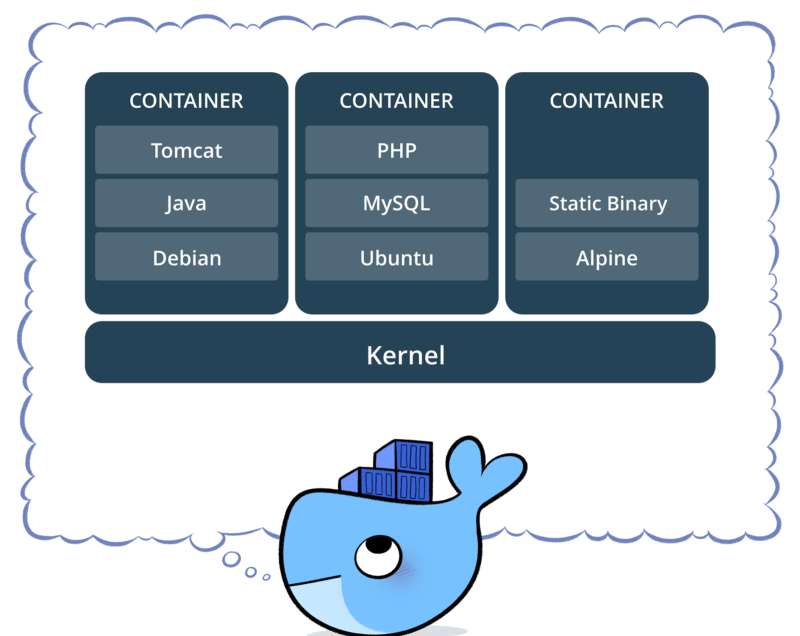
In short; Docker images are the execution and packaging of all operations in the Dockerfile file. Docker container is formed when the prepared image is taken and operated in an isolated environment. An image is needed to create the Docker container.
Let’s Get Our Hands Dirty!
Now we need to get our hands a little dirty to learn about Docker. There are some parameters we need to use Docker, let’s examine them;
Let’s take an Ubuntu image from Docker Hub and container it on our own computer.
$ docker create -it ubuntu:16.04 bashThere are two commands here that seem different to us. “-itThe ” parameter provides a simultaneous connection between your terminal and the container you created. The last one is “bashThe ” argument is the command you want to run when the container starts. Here we want the “bash” command to be run in Ubuntu. Apart from these, “ubuntu:16.04In the ” section, we state that we want to convert version 16.04 of the Ubuntu image in Docker Hub into a container.
$ docker ps -aWe can find out the status of our containers using the command above. “docker psThe ” command lists only actively running containers. “-awe can also list containers created and stopped if we use the ” parameter.
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
200e7e34d036 ubuntu:16.04 “bash” 4 seconds ago Created compassionate_lumiere
We created the container and now we need to run it, for this it is only “startJust write ”.
$ docker start 200e7e34d036We can see the container status by listing it again. (This time we can see our container without the “-a” parameter.)
$ docker psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
200e7e34d036 ubuntu:16.04 “bash” 4 seconds ago Created compassionate_lumiere
$ docker attach 200e7e34d036“ aboveattachwe can connect to the container with the ” command. We are now connected to our container containing the Ubuntu operating system and we can do whatever we want. “ to log out after check-inexitYou can use the ” command.
Note: Docker containers operate as “sudo” by default. This means that there is no sudo command in the containers. Every command you run in the container will automatically work with sudo powers.
Docker Usage Example, How to Use Docker?
Docker is generally used a lot in publishing web applications. We will examine it by making a simple and quick example.
We said that all containers we created with Docker work in isolation. When you delete the container, everything is deleted.
“$ docker rm 200e7e34d036 The ” command allows deletion of the created container.What’s in the Container Stays in the Container!
“What is in the container remains in the containerthe ” philosophy can be annoying in some situations. How do we store data if everything is deleted? We need a lifeguard here, and Docker comes to our rescue and won’t leave us alone in this regard. Docker allows us to map the directories on your own computer with the directories in the container. We think this last sentence brings joy to your heart.
$ docker create -it -v $(pwd):/var/www ubuntu:latest bashThe command we wrote above is “-v” in the container with the directory we are in via the “ parameter/var/wwwconnects directory ”.
Now “runeIt’s time for us to learn the ” command. The command we will use most on Docker is “docker runit is the ” command. The run command does alone what the “create” and “start” commands do. When we use the run command, first the container is created like the “create” command and then it runs the container it created like the “start” command.
$ docker run -it -d ubuntu:16.04 bash“-dThe ” parameter allows the created container to start running in the background.
Let’s Tear Down the Walls!
It is time for us to practically stretch the philosophy that what is in the container remains. Now a small static page on the physical machine is located in the container Nginx We will broadcast it with HTTP web server software. Create a directory and click below HTML to the directory where you created the codes index.html save with name.
<html>
<head>
<title>Docker Demo Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class=”container”>
<h1>Let's Learn Some Docker</h1>
<p>This page is published using nginx.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>Next up is to publish this static file with Nginx in the container. The following command will help us do this.
$ docker run –name seccops_nginx -v $(pwd):/usr/share/nginx/html -d -p 8080:80 nginxYou see different parameters in the command above. “–nameThe ” parameter allows us to name the container. “-pused in container with ” parameter To port 80, on your host machine via port 8080 it ensures reachability.
All changes we make in the index.html file we create on our computer will change simultaneously within the container. Likewise “ in container/usr/share/nginx/htmlany file that can be added to the ” directory will also be transferred to your physical computer.
We can stop the Docker container you created with the following command.
$ docker stop <container id>