Understanding IP Spoofing: A Comprehensive Guide to This Cyber Threat
What is IP Spoofing?
IP spoofing, also known as IP address forgery, is a technique used by hackers to gain unauthorized access to computers. This concept first emerged in academic publications in the 1980s. Essentially, IP spoofing involves disguising a malicious source to make it appear as a trusted source, often used to mask the origin of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
How IP Spoofing Works
In IP spoofing, cyber attackers hide their identity to launch cyber attacks on victims. In DDoS attacks, masking the source makes it difficult to detect or block the cyber attack. The TCP packet header contains information such as port and number, while Ethernet headers include specific details like source and destination MAC addresses. For instance, if a packet is encrypted for security (e.g., TLS), it should have a TLS header. An attacker can modify the IP header to include a different address, making the packet appear as if it was sent from another machine. The targeted computer cannot see the real source and responds to the altered IP address in the header information.
Theoretically, IP spoofing can be performed on all protocols. However, in practice, it is feasible in applications using UDP but not in those using TCP. This is because TCP requires a three-way handshake, and the sequence number in the packet header is unpredictable.
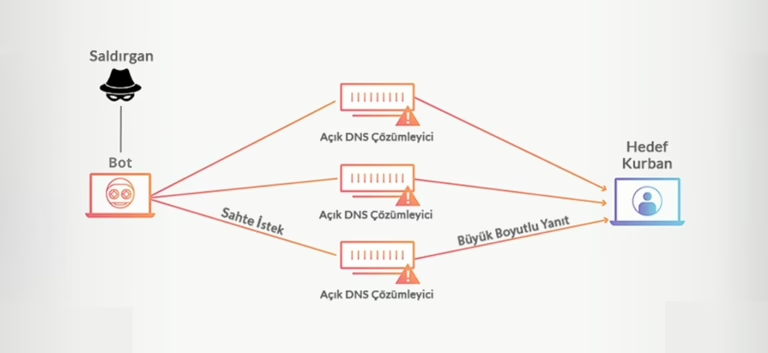
IP Spoofing in DDoS Attacks
IP spoofing is frequently used in DDoS attacks. The goal of such attacks is to overload the target computer with excessive traffic, preventing it from responding. Each spoofed packet appears to come from a different address, making filtering more challenging.
An intruder using IP spoofing sends messages to a computer system containing an IP address that appears to come from a different IP address. If the goal is to gain unauthorized access, the spoofed address makes the target see the connection as coming from a trusted host.
Executing an IP Spoofing Attack
To successfully execute an IP spoofing attack, cyber attackers must first identify the IP address of a machine that the target system trusts. Hackers can use various techniques to find a trusted host’s IP address. Once they have this trusted IP address, they can alter the packet headers, making the packets appear as if they are coming from this trusted host.
Unlike many other types of attacks, IP spoofing was known to be theoretically possible by security experts before it was actually used in a real attack. Although the concept behind this technique has been known for some time, Robert Morris demonstrated its practical feasibility by identifying a security vulnerability in the TCP protocol.
Preventing IP Spoofing
IP spoofing attacks are not as common as they used to be, primarily because organizations have become more security-conscious. Many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) now block IP spoofing. However, IP spoofing remains an effective form of attack in today’s world.
Methods to Counter IP Spoofing
Configuration Examples
Preventing IP Spoofing on Linux Operating Systems
To prevent IP spoofing on an Ubuntu server, you need to configure it properly. Log in to your Ubuntu server and run the command sudo nano /etc/host.conf. The host configuration file will open. The host.conf configuration file contains configuration information specific to the resolver library. Change the line that says multi on to nospoof on. At this point, adding the nospoof value to the DNS resolver library attempts to prevent host name spoofing.
For more detailed information, you can refer to resources like US-CERT’s guide on IP spoofing.