What is Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security?
Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity is revolutionizing threat detection and response with machine learning algorithms that analyze millions of security events per second and identify patterns that humans cannot perceive. According to IBM’s Artificial Intelligence Security Report, businesses using artificial intelligence in cyber security reduce incident response times by 70% and reach a threat detection rate of 98%. This technology processes large data sets to predict cyber attacks, automate defenses, and adapt to evolving threats faster than traditional security methods. businesses implementing AI-driven security save 150 billion dollars annually thanks to improved threat prevention and reduced breach costs. Security teams leverage artificial intelligence to combat deepfakes, automated phishing, and advanced cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure.
What is Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security?
In cybersecurity, artificial intelligence uses artificial intelligence technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing to protect systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. This technology analyzes large volumes of data, identifies cyber attack patterns, and makes security decisions at a speed beyond human capabilities. Artificial intelligence transforms cybersecurity from reactive defense to proactive threat hunting through continuous learning and adaptation.
Modern AI systems process billions of security events every day in enterprise environments. Machine learning models recognize similar patterns in real time by learning from past events. Deep learning identifies detailed threats by processing complex, layered data. Natural language processing analyzes emails and communications for phishing indicators.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security
The benefits of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity include:
Faster detection of underlying vulnerabilities
Artificial intelligence-supported solutions quickly detect vulnerabilities in systems, reducing the opportunity for cybercriminals to exploit these vulnerabilities. Research shows that artificial intelligence can shorten the time it takes to detect vulnerabilities from weeks to hours or even minutes.
Better risk detection and informed security measures
AI-powered analytics enables businesses to gain more in-depth knowledge of their security situations and implement targeted, data-driven security measures.
24-hour monitoring and threat mitigation
AI-based cybersecurity tools provide 24/7 automatic monitoring and significantly reduce the time it takes to respond to security incidents, allowing businesses to more effectively prevent or limit the impact of breaches.
Reducing the burden on cybersecurity experts
AI automates routine tasks, allowing security professionals to focus on more complex challenges.
Improved efficiency and cost effectiveness
AI-powered cybersecurity solutions streamline processes, minimize human errors, and reduce dependence on manual labor.
Advanced incident response
AI-powered tools can analyze and prioritize security incidents, allowing businesses to respond to breaches more quickly and effectively.
Scalability and adaptability
Artificial intelligence-based cybersecurity solutions can be adapted and scaled to meet the changing needs of businesses, providing a more resilient and agile security infrastructure that can grow with the organization.
Proactive threat hunting
AI-powered solutions can actively seek out potential threats in a business’s digital environment and detect and address risks before they literally escalate into cyber attacks.
Limitations of AI Use in Cyber Security
AI does not help against unique threats. It is often trained on historical data and models. As a result, it may have difficulty detecting and responding to completely new or extremely complex threats never seen before. AI won’t help you find creative ways to attack a system. AI can detect known vulnerabilities and patterns of cyberattacks, but it may not be effective in discovering new attack vectors that require unorthodox thinking or human intelligence.
AI is also a great new tool for cybercriminals. As AI advances in security, it can also be used by hackers to create more powerful threats, such as developing advanced malware or automating large-scale attacks. This could accelerate the race between cybersecurity experts and cybercriminals. The effectiveness of AI-powered cybersecurity solutions depends largely on the quality and quantity of data used for training. False or biased data can potentially undermine the reliability of the system by leading to false positive or negative results.
Comprehensive data collection and analysis required for AI-based cybersecurity can raise privacy and ethical concerns, especially when it comes to sensitive personal or corporate information. Implementing AI-based solutions within existing cybersecurity infrastructures can be complex, as businesses need to ensure seamless integration and compliance with their existing systems and processes.
Artificial Intelligence Applications in Cyber Security
The unique strengths of various types of AI are used in versatile ways to improve your digital protection. From simple solutions using a single type of neural network to more complex systems integrating multiple neural networks, AI offers a range of precise and powerful security tools to overcome a variety of challenges.
In the list below you can find examples of uses using AI-driven technologies:
Password Protection and Authentication
Artificial intelligence transforms password security with advanced authentication mechanisms that prevent credential-based attacks. CAPTCHA systems use artificial intelligence to separate people from bots and block 99% of automatic login attempts. Facial recognition and fingerprint scanners provide layers of biometric authentication that cannot be copied or stolen.
AI-powered multi-factor authentication analyzes user behavior patterns during login. Systems detect anomalies such as unusual locations, devices, or timings that indicate credentials have been compromised. Behavioral biometrics tracks writing patterns, mouse movements, and navigation habits specific to each user. AI prevents brute force attacks by identifying systematic password guessing attempts. Machine learning algorithms recognize credential-filling patterns in which hackers use stolen passwords across multiple sites. Systems automatically lock accounts and alert security teams when they detect suspicious authentication activity. Password strength analysis implements complex password policies using AI and prevents widespread password use.
Phishing Detection and Prevention
Phishing detection evolves exponentially through AI analysis of email content and context. Machine learning detects 95’% of phishing attempts by examining message metadata, sender reputation, and communication patterns. Natural language processing detects social engineering tactics such as urgency, fear, and impersonation. AI recognizes advanced spear-phishing attacks targeting managers and high-value employees. Algorithms detect CEO fraud attempts by analyzing spelling styles and communication patterns. Systems flag emails containing remittance requests, credential changes, or sensitive data that deviate from normal business processes.
Real-time URL analysis prevents users from accessing malicious websites. AI examines connection targets, checks domain reputation, and detects typosquatting attempts. Sandboxing technology destroys suspicious attachments in isolated environments before delivery. AI-powered email authentication protocols verify sender legitimacy through DMARC, SPF, and DKIM verification.
Vulnerability Management
AI-powered vulnerability management identifies and prioritizes security vulnerabilities in enterprise infrastructure. User and asset behavior analysis (UEBA) determines key activity patterns for devices, servers, and users. Systems detect abnormal behavior that indicates zero-day exploits before an official vulnerability disclosure is made. Businesses strengthen their security status with machine learning-supported vulnerability assessment solutions. Continuous vulnerability scanning reveals misconfigurations and outdated software. AI identifies exploitable vulnerabilities by linking threat intelligence to asset inventories. Predictive analytics predicts vulnerabilities that hackers are likely to target based on past patterns.
Automatic patch management ensures timely removal of vulnerabilities. AI plans updates during maintenance, tests compliance, and verifies successful deployment. Systems prioritize critical patches based on likelihood of abuse and potential impact. Risk scoring algorithms evaluate the severity of the vulnerability by taking into account the business context and threat environment.
Network Security
Network security takes advantage of AI’s ability to learn traffic patterns and propose optimal policies. Systems analyze network topology, identify legitimate connections, and flag potentially malicious behavior. AI implements zero trust principles by continuously validating each connection attempt. Businesses can validate their network defenses through penetration testing phases that simulate AI-powered cyberattacks.
Machine learning reduces policymaking time by 75% with automated recommendations. AI determines which workloads belong to specific applications despite inconsistent naming conventions. Systems propose segmentation strategies that minimize attack surfaces while maintaining operational efficiency. Real-time traffic analysis detects lateral movements and data leak attempts. AI identifies command and control communications hidden in legitimate traffic. Behavior analysis recognizes insider threats and compromised accounts through unusual access patterns. AI-powered network forensics rebuild chains of attacks for incident investigation.
Behavior Analysis
AI-powered behavior analysis creates comprehensive profiles of applications, devices, and users across networks. Systems process large volumes of data to identify normal activity references. Incoming data is analyzed by comparing it with profiles to detect potentially harmful deviations. Machine learning identifies evolving threats that signature-based systems overlook. AI recognizes polymorphic malware that changes its properties to evade detection. Behavior analysis captures fileless attacks that run entirely in memory without traditional indicators.
Threat hunting becomes proactive to the reagent thanks to AI automation. Systems constantly seek out hidden threats without human intervention. Advanced persistent threats arise through correlation of subtle indicators over long periods of time. Anomaly detection algorithms identify insider threats through unusual data access models or privilege escalation attempts.
Artificial Intelligence and Cyber Crimes
While artificial intelligence has been implemented in many ways to improve cybersecurity, it is also used by cybercriminals to launch increasingly advanced attacks at an unprecedented rate. In fact, 85’% of security experts who have seen an increase in cyber attacks in the last 12 months attribute this increase to hackers using artificial intelligence. Cybercrime is estimated to reach an annual cost of 10.5 trillion dollars by 2025, and AI is predicted to play a significant accelerating role in this increase.
Below are a few examples of AI being used in cybercrime:
Businesses that use artificial intelligence and automation extensively to improve their cybersecurity capabilities will be best positioned to defend against cybercriminals using artificial intelligence as a weapon. According to a study by the Capgemini Research Institute, 69’% of executives stated that artificial intelligence increases the efficiency of cybersecurity analysts in their businesses. 69’% also believe that artificial intelligence is necessary to respond effectively to cyber attacks.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security
The future of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity includes machine-to-machine warfare, in which artificial intelligence systems engage in real-time combat with hostile artificial intelligence. Security operations centers will become advanced platforms that make tactical decisions at machine speed. By 2026, autonomous AI agents will investigate vulnerabilities, discover vulnerabilities, and fix them before they are exploited. According to Microsoft’s Artificial Intelligence Security Research, businesses should be prepared for AI-driven threat environments.
Quantum computing threatens existing encryption methods and requires quantum-resistant artificial intelligence security systems. Businesses should be prepared for “now collect encrypted data, then decrypt” attacks, where hackers collect encrypted data for future quantum decryption. Artificial intelligence will develop new encryption methods that are resistant to quantum attacks. Productive AI creates realistic attack simulations to test defenses. Systems produce synthetic threats that mimic real-world attack patterns to train detection models. Predictive analytics anticipates attack scenarios, enabling proactive measures to be taken before threats occur.
Agentic AI works semi-autonomously with human analysts in security operations centers. These agents carry out classification, investigation and intervention actions of warnings without human intervention. Businesses that implement Agentic artificial intelligence report a 70% reduction in incident response times. New roles are emerging, such as AI security ethicists and machine learning defense experts. Experts need to understand AI-specific vulnerabilities such as prompt injection, model extraction, and data poisoning. Continuous training is essential for security teams to effectively manage emerging threats from artificial intelligence.
Most Asked Questions
How is artificial intelligence used in cyber security?
In cybersecurity, artificial intelligence is used by automating repetitive, manually intensive and difficult-to-completion tasks to complement the efforts of experts. Because AI can analyze large volumes of data, detect patterns that people may miss, and adapt and improve their capabilities over time, it excels in threat detection, threat management, threat response, endpoint security, and behavior-based security.
What is AI responsible for cybersecurity?
AI responsible for cybersecurity means designing and using safe, secure and reliable AI in the industry. The goal is to increase transparency and reduce risks such as AI bias by encouraging the adoption of certain best practices, such as red team testing.
How are AI and machine learning changing the cybersecurity landscape?
AI and machine learning are used to strengthen cybersecurity in unprecedented ways, such as flagging hidden anomalies, identifying cyber attack vectors, and automatically responding to security incidents. It is also used to launch increasingly advanced and frequent cyber attacks.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing every aspect of our lives. From the ads we see, to how we unlock our devices, to how we drive our cars (or, very soon, how they drive us); nothing is off-limits. Nowhere is the impact of AI more apparent and crucial than in cybersecurity, where by the end of 2021, global cybercrime damages are predicted to cost up to $6 trillion.
The need for new technology, such as artificial intelligence, has never been more vital than it is today for cybersecurity. Here are 5 ways it is likely to help.
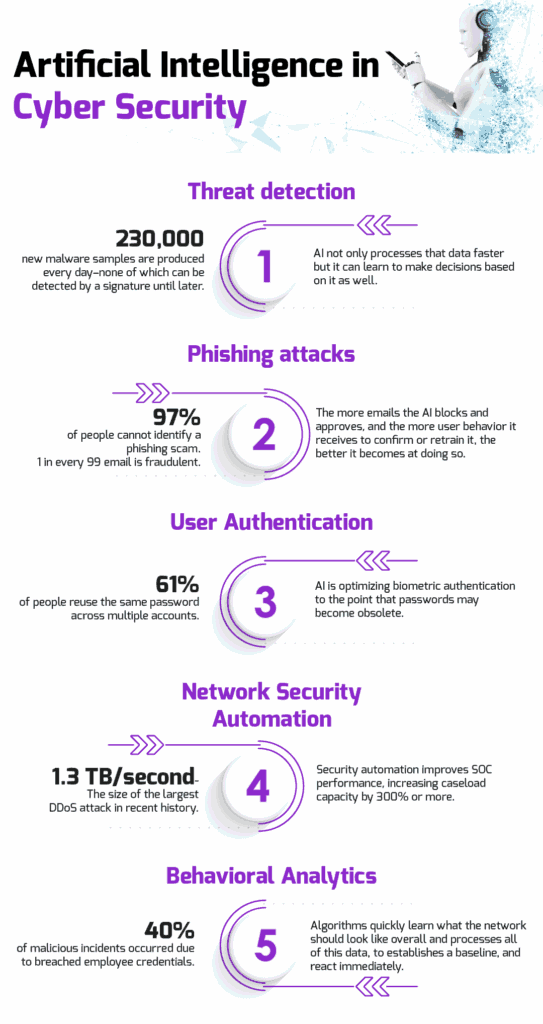
Threat Detection
The traditional way of detecting threats is based on the past. Once the malware has been recognized and cataloged, it can be assigned a signature so that Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) know what to look for in the future. This works great against known threats, but what about new ones? It is estimated that 230,000 new malware samples are produced every day–none of which can be detected by a signature until later. This gap between when a new threat is detected to when it is categorized and can be prevented leaves an open window of vulnerability.
Artificial intelligence not only processes that data faster but it can learn to make decisions based on it as well. It is more accurate at detecting threats, creating less false-positives as it learns, than any human being is. Because of this, it is more adept at improvising and reacting to the endless deluge of data coming in.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing has been in existence since the early days of the internet. If it is so old, why is it still so prevalent? Because it still works. 97% of people cannot identify a phishing scam while 1 in every 99 emails are exactly that–a phishing attack. Artificial intelligence is already being used to mitigate the issue.
Artificial intelligence is able to analyze every aspect of an email, from the source to the content to the time it was sent, and react almost instantaneously to that information. It doesn’t just rely on asking, what domain did this come from? It can take into account the domain, the header, the geographic location, whether it was sent through a VPN or proxy, and compare all of that combined information against a baseline. The more emails the AI blocks and approves, and the more user behavior it receives to confirm or retrain it, the better it becomes at doing so.
Looking for career tips from Chicago’s top IT staffing team?
User Authentication
It is common knowledge that users (i.e., people) are usually the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain. Poor password habits, like reusing passwords or not changing default ones, are some of the most dangerous vulnerabilities most organizations have to face.
Artificial intelligence is optimizing biometric authentication to the point that passwords may become obsolete. Most modern mobile devices are able to use fingerprint or facial recognition to unlock a device, but today it is used mostly for convenience. Users are still hesitant to completely relinquish their login capabilities to a somewhat flawed biometric system. As these AI-power technologies get better, and new ones like voice recognition are perfect as well, passwords become less and less important.
Network Security Automation
Setting security policies and outlining network topography are two of the most time-consuming tasks of many cybersecurity engineers. That’s because most of it is done manually.
Artificial intelligence is able to automate quite a bit of this. It can monitor a network usage behavior (who accesses what, when, using how much bandwidth, etc.) and can make recommendations based on that data. A human can then review those recommendations, often much more accurate than they could have produced on their own, and make changes to policies and procedures as necessary.
Behavioral Analytics
Perhaps the most powerful way artificial intelligence can improve cybersecurity is through behavioral analytics. Seasoned cybersecurity engineers get a ‘feel’ for the networks they’re responsible for. They know them like the back of their hand—the intricacies, the nooks and crannies, the hidden compartments–no one understands these better.
Except, maybe, artificial intelligence.
Algorithms quickly learn what the network should look like overall. How much bandwidth is used on a Tuesday afternoon compared to Sunday morning? What geographic location devices are usually logging in from? What applications are accessing which ports? The algorithm processes all of this data, establishes a baseline, and can immediately react. Not only to a single event or parameter, but to a combined collection of behaviors.






