Understanding DNS Hijacking: A Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Your Online Security
Understanding DNS Hijacking
To comprehend DNS Hijacking, it’s essential to grasp the concept of DNS and its functionality. DNS, or Domain Name System, is akin to the internet’s phonebook. It translates human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, facilitating our navigation of the web.
The Role of DNS
Every website and server on the internet has a unique IP address, typically composed of 32 bits under the IPv4 standard, divided into four octets. Remembering these numerical addresses for every website we visit is impractical. Hence, domain names were introduced, providing a user-friendly alternative to IP addresses.
When you enter a domain name in your browser, a DNS server translates this name into the corresponding IP address. This process, known as DNS resolution, is crucial for directing your request to the correct server.
DNS Hijacking Explained
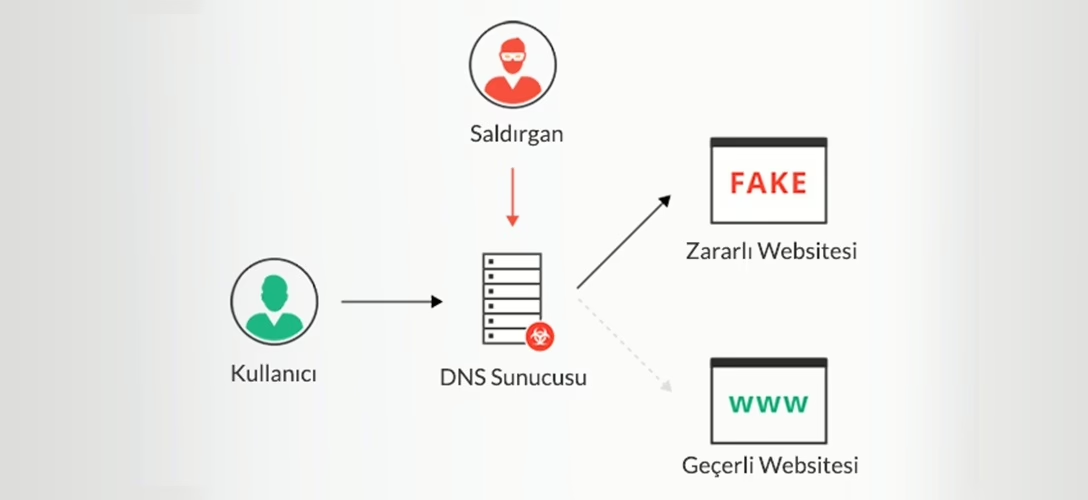
DNS Hijacking, also known as DNS redirection, is a malicious practice where attackers manipulate DNS resolution to redirect users to harmful websites. This can be done for various purposes, including:
- Pharming: Redirecting users to advertisement sites for financial gain.
- Phishing: Stealing users’ personal and financial information.
How DNS Hijacking Works
In a typical DNS resolution process, your computer (client) sends a request to a DNS server to resolve a domain name. The DNS server then responds with the correct IP address, and your computer connects to the desired website.
However, in a DNS Hijacking scenario, attackers interfere with this process. They might compromise a DNS server and alter its records, causing it to return incorrect IP addresses. Consequently, users attempting to visit legitimate websites are redirected to malicious ones.
This redirection can be achieved through various methods, such as DNS cache poisoning, where attackers corrupt the DNS server’s cache with false information. Another method is by exploiting vulnerabilities in routers or local networks to alter DNS settings.
Types of DNS Hijacking Attacks
There are several types of DNS Hijacking attacks, including:
- Local DNS Hijacking: Attackers infect a user’s computer with malicious code that alters the computer’s DNS settings, redirecting the user to harmful websites.
- Router DNS Hijacking: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in routers to change DNS settings, redirecting all users connected to that router to malicious sites.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) DNS Attacks: Attackers intercept and alter communication between a user’s computer and a DNS server, redirecting the user to malicious sites.
- Rogue DNS Server: Attackers compromise a DNS server and alter its records to redirect users to malicious sites.
Preventing DNS Hijacking
Protecting yourself from DNS Hijacking involves several best practices:
For more information on phishing and how to protect yourself, you can visit this authoritative guide on recognizing and avoiding phishing scams.
Conclusion
DNS Hijacking is a serious threat to online security. By understanding how it works and implementing preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to these attacks. Always stay vigilant and prioritize your online safety.